Detecting and Treating Mesothelioma with Imaging and Diagnosis
Writer : Dr. Naskan
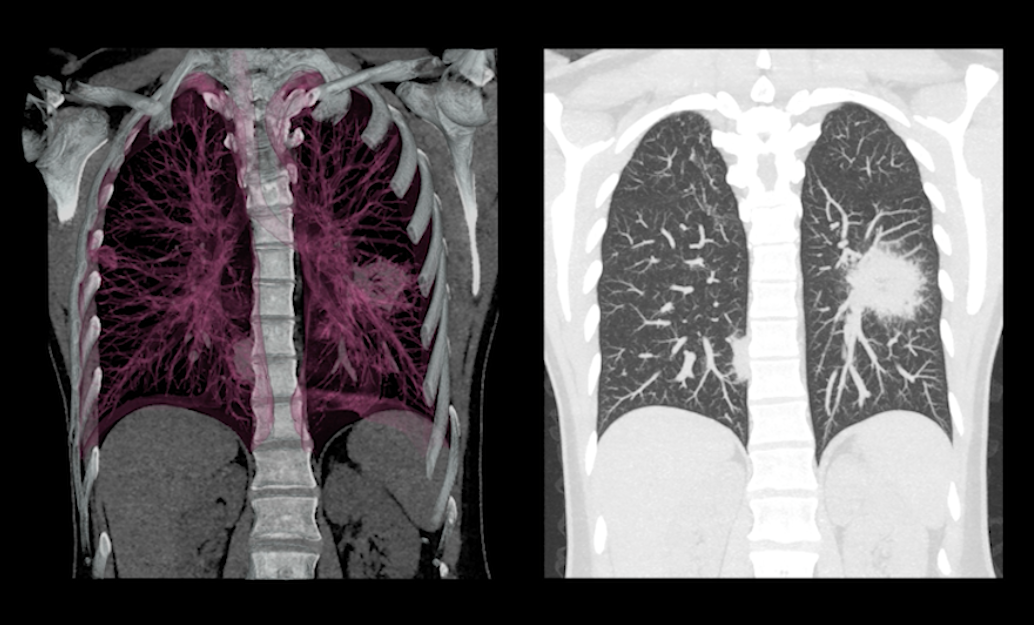
Detecting and Treating Mesothelioma with Imaging and Diagnostics, An overview of the diagnostic modalities and imaging findings for mesothelioma.
In 1909, just a few years after the invention of medical X-ray imaging, the term "mesothelioma" was coined. Numerous studies and thousands of autopsies later, the term was coined to describe the link between asbestos and cancer. In 1931, as X-ray technology advanced, the framework for diagnosing and understanding mesothelioma was established.
Cardiothoracic surgeon Sai Yendamuri, M.D., FACS, chair of the Department of Thoracic Surgery at Roswell Park Cancer Institute in Buffalo, New York, said, "Mesothelioma is an unusual tumor, both in its genesis and its clinical presentation." He specializes in cancers of the chest, lungs, and esophagus, including mesothelioma. –
He warned that the disease can be difficult to identify.. X-rays, MRIs, CTs, and nuclear scans using positron emission tomography (PET) are the most commonly used imaging modalities for diagnosing mesothelioma today. Yendamuri explained that imaging is typically performed once symptoms are evident and before an invasive biopsy is performed.
The Use of Chest X-Rays in Diagnostic Procedures
If you have symptoms of mesothelioma or another disease affecting the heart or lungs, an x-ray may be the first imaging tool you use to look for a cause for concern. Chest X-rays may be used as an initial screening for those at risk of developing mesothelioma, such as factory or construction workers and veterans with significant asbestos exposure.
There are no specific radiographic findings for mesothelioma, and they can be seen in other diseases such as metastatic carcinoma, lymphoma or benign asbestos disease even under ideal circumstances. Radiographs may miss small malignant pleural effusions, but large pleural effusions can obscure thickening or masses in the pleural cavity.
As for the importance of an X-ray in the detection of pleural effusions as an early sign of mesothelioma, Yendamuri stated. Early detection of mesothelioma necessitates a thorough knowledge of the disease's symptoms and signs. It is common for an advanced imaging test to be performed after abnormal chest radiographs.
These are the most common radiological findings in mesothelioma imaging exams, as stated by Yendamuri:
- Plaque-like or nodular pleural thickening
- Unilateral pleural effusion
- Loss of volume in the hemithorax
- Compression of the lung parenchyma, diaphragm elevation, narrowing of the intercostal space, and mediastinal shift toward the tumor are all symptoms of an encased lung.
- Fissures that have been thickened and irregularly shaped by tumor extension.
- Plaques are found in approximately 20% of patients with malignant mesothelioma.
Staging Tumors with CT
According to Yendamuri, patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma require CT scans to stage tumors. With the 3-D CT scans, you get a far more detailed view and a detection sensitivity of more than 90 percent.
Although it is true that appearances can be subjective, he asserted that this is largely due to the operator. CT scans are still the best imaging study for diagnosing malignant pleural mesothelioma, even though they are less effective for detecting peritoneal mesothelioma. Mesothelioma diagnosis can either be confirmed or ruled out entirely by a scan, which can also help estimate the extent or stage of the disease.
CT images can also help determine if the tumor can or should be surgically removed.
CT scans for mesothelioma typically show the following:
- Invasion of the diaphragm, mediastinum, and chest wall by the tumor.
- Nodular thickening of the pleura, thickening of the pleura greater than one centimeter, thickening of the mediastinal pleural surface, and thickening of the pleura that is concentric
Mesothelioma patients can benefit from MRIs.
Some patients may benefit from MRI exams in addition to CT scans because they allow for better soft tissue delineation and imaging in the sagittal and coronal planes. According to Yendamuri, MRI scans are better at detecting mesothelioma metastasis than CT scans because CT scans have a higher rate of missing metastasis.
Additionally, patients who are sensitive to the contrast dyes used in CT scans can benefit from MRI scans as an alternative to those tests. Tissue biopsy is the only way to be sure that a patient has mesothelioma after a CT or MRI scan.
MRI findings that are common include:
- An isolated chest wall, endothoracic fascial, and dilated diaphragm invasion.
- Muscle T1 isointensity signals in the sternum
- The injection of gadolinium results in slightly elevated signals on T2-weighted images as well as slightly enhanced T1-weighted images
Mesothelioma patients can benefit from PET scans.
In the case of malignant pleural mesothelioma, a PET nuclear scan can be useful in assessing the prognosis of patients because it is sensitive enough to detect slight metabolic increases and thus can detect extremely small tumor collections throughout the body.
PET scan images have a low resolution, which is why most modern cancer centers use PET and CT scans in combination for dual imaging. Peritoneal mesothelioma diagnosis and staging can benefit from the use of this imaging technology, but it isn't essential.
The following are common PET findings:
- lymph node involvement, tumors, and metastases
- Pleural mesothelioma can be distinguished from benign pleural lesions.
Only a Small Part of Mesothelioma Is Diagnosed.
Remember that diagnosis is only one part of the treatment timeline for mesophageal cancer despite how difficult it can be to get a definitive diagnosis. Mesothelioma is diagnosed and staged through imaging tests. As Yendamuri explained, images can help doctors determine which treatments are most effective.
When mesothelioma is discovered during the course of treating a pleural effusion, "more therapeutic treatment options should hopefully be available," Yendamuri urged.
Read more:
- Detecting And Treating Mesothelioma With Imaging And Diagnosis
- Mesothelioma Of The Pleura
- Mesothelioma Prognosis And Prolonged Life Expectancy
- Mesothelioma
- Peritoneal Mesothelioma Symptoms Diagnosis And Treatment Options
Mesothelioma